Working Time
- Mon-Sat 10:00 – 19:00
Contact Info
-
+90 542 512 51 64
Ask the Experts
Cataract
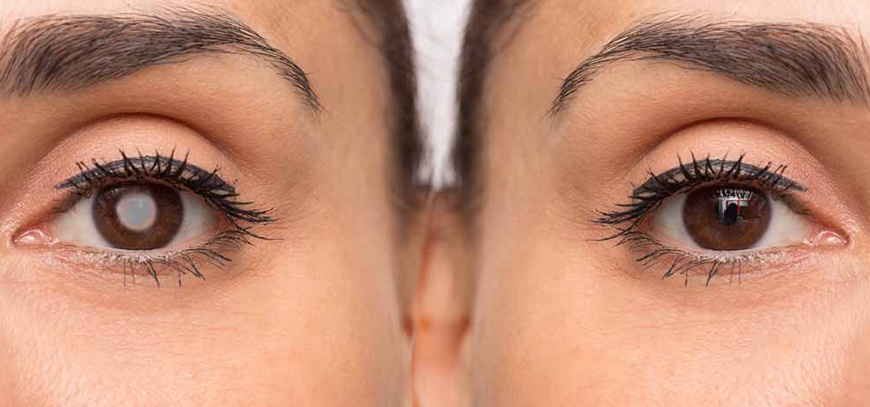
A cataract is a cloudy or opaque area in the normally clear lens of the eye. Depending upon its size and location, it can interfere with normal vision.
Most cataracts develop in people over age 55, but they occasionally occur in infants and young children or as a result of trauma or medications. Usually, cataracts develop in both eyes, but one may be worse than the other.
The natural lens is located inside the eye behind the iris, the colored part of the eye. Normally, the lens focuses light on the retina, which sends the image through the optic nerve to the brain. However, if the lens is clouded by a cataract, light is scattered so the lens can no longer focus it properly, causing vision problems. The lens is made of mostly proteins and water. The clouding of the lens occurs due to changes in the proteins and lens fibers.
Types of Cataracts
The lens is composed of layers, like an onion. The outermost is the capsule. The layer inside the capsule is the cortex, and the innermost layer is called the nucleus. A cataract may develop in any of these areas. Cataracts are named for their location in the lens:
- A nuclear cataract is located in the center of the lens. The nucleus tends to darken with age, changing from clear to yellow and sometimes brown.
- A cortical cataract affects the layer of the lens surrounding the nucleus. The cataract looks like a wedge or a spoke.
- A posterior capsular cataract is found in the back outer layer of the lens. This type often develops more rapidly.
The Procedure
Cataract surgery involves removing the natural lens of the eye and replacing it with an artificial lens. The artificial lens requires no care and can significantly improve vision. Some artificial lenses have the natural focusing ability of a young healthy lens. Once a cataract is removed, it cannot grow back.
Two approaches to cataract surgery are generally used:
- Small-incision cataract surgery involves making an incision in the side of the cornea (the clear outer covering of the eye) and inserting a tiny probe into the eye. The probe emits ultrasound waves that soften and break up the lens so it can be suctioned out. This process is called phacoemulsification.
- Extracapsular surgery requires a somewhat larger incision in the cornea so that the lens core can be removed in one piece. The natural lens is replaced by a clear plastic lens called an intraocular lens (IOL). When implanting an IOL is not possible because of other eye problems, contact lenses and, in some cases, eyeglasses may be an option for vision correction.
As with any surgery, cataract surgery has risks from infection and bleeding. Cataract surgery also slightly increases the risk of retinal detachment. It is important to discuss the benefits and risks of cataract surgery with our online consultans. Other eye conditions may increase the need for cataract surgery or prevent a person from being a cataract surgery candidate.
Cataract surgery is one of the safest and most effective types of surgery performed in Turkey today. Approximately 90% of cataract surgery patients report better vision following the surgery.
If the surgeon has administered medication to help you relax during the surgery, you may be a little groggy afterward and will usually be asked to rest in a designated recovery area for 30 minutes to an hour. A protective shield will be placed over the eye or eyes in which the surgery was performed, and your guide will help you get back to your hotel in our VIP car. Although many patients report experiencing clear vision just several hours after the surgery, others may not see results for several days to a week.
Please feel free to reach out to us at your convenience on WhatsApp number +90542 512 5164 or fill out our online contact form to schedule a consultation if you’d like more information on how cataract surgery can enhance your quality of life.
Cataract surgery is usually very quick. The procedure itself takes about a maximum of 20 to 30 minutes from start to finish.
Although you’ll likely be awake during the procedure, it is not painful because you’ll be given a local anesthesia. You may experience slight discomfort, but intense pain is uncommon.
